GEM LUMINESCENCE
Gem Luminescence - a guide to reactions
Photoluminescence (PL) is the emission of light caused by irradiation with photons. The emitted light is usually of a longer wavelength, and has lower energy, than that of the absorbed radiation.
Both phosphorescence and fluorescence are forms of photoluminescence. Phospholuminescence persists for seconds or minutes after the illuminating source has been extinguished whereas the glow of fluorescence disappears almost immediately the illuminating source is extinguished. Most gems exhibit a characteristic photoluminescence of visible light in response to ultra-violet irradiation. Gemmologists use both short-wave (255 nm) and long-wave (365 nm) to probe the reaction of gems and note the colour and intensity of fluorescence and phosphorescence.
Diamonds grown by high-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) methods represent the vast majority of near-colourless synthetic diamonds that may be found in jewellery. These diamonds exhibit the phenomenon of phosphorescence after exposure to short-wave ultra-violet light.
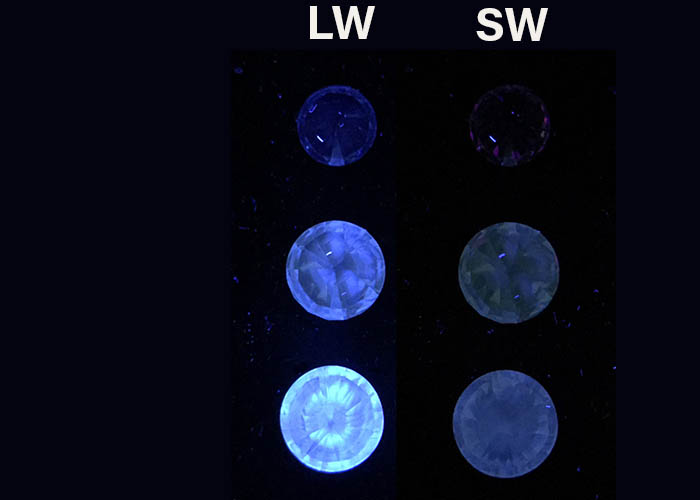
Natural diamonds
Natural diamonds mostly fluoresce a blue colour in LW UV, with a weaker intensity fluorescence under SW UV. The intensity ranges from very strong to nil in instances where the impurity nitrogen state quenches fluorescence. A few percent of natural diamonds fluoresce yellow while even lower percentages fluoresce green, orange, red or white.
Coloured diamonds also exhibit characteristic reactions as shown in a PL reaction chart (download PDF file).
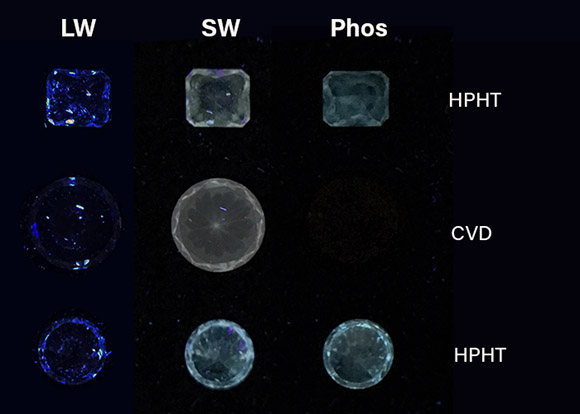
Synthetic diamonds
Colourless and near-colourless lab-grown diamonds are Type II (nitrogen free) and do not have the defects responsible for the blue fluorescence in natural diamonds. They typically have a stronger fluorescence intensity under SW UV. In the case of HPHT-grown diamonds, they will usually phosphoresce after exposure to SW UV. Coloured LGDs tend to have characteristic reactions as seen in the PL reaction chart (download PDF file).
Other gems
Other gemstones can also be examined under UV to help determine is they are synthetic or treated, and in some case their origin may be infered. Some gemstones that have been effectively examined using a PL or Jewellery Inspector include:
- Rubies and emeralds
- Jade
- Opal
- Amber